SREB Region Lags Behind in New Skills Report
In the new Coursera Global Skills Report, the United States ranked 78 out 100 countries on job skills observed from Coursera’s learner base. The three job-relevant skill domains compared in the report were business, technology and data science.
The Coursera Global Skills Report aims to help leaders in business, government and higher education understand the rapidly changing skills landscape across the world and draws on data from its learners.
In 2019, the Southern Regional Education Board explained in its Economic Outlook The Potential Impact of Automation and AI rather than entire jobs disappearing, it is more likely that certain aspects of jobs will be automated as technology advances. Adults with the lowest level of skills — typically those with a high school diploma or less — are most vulnerable to these changes. But more and more working adults need to adapt and raise skill levels to stay competitive in the workforce. This has become increasingly true with the introduction of generative AI, such as ChatGPT, and further advancement in automation.
Coursera observed 100 countries from its registered learner base of more than 124 million learners and compared the countries across the three skill domains — business, technology and data science. Examples of the skills observed include proficiencies in strategy and operations, leadership and management, computer programming, software engineering, data analysis and machine learning.
The framework of the report is organized by three questions:
- How proficient is the workforce in critical job skills?
- What skills are popular among learners in the country or region?
- How much of the workforce is preparing for in-demand, digital roles?
The United States ranked 78 out of the 100 countries included in the report. While the United States does compete with top countries’ business skills proficiencies, skill proficiencies in technology and data science need further investment and improvement.
| Global Ranking | Country | Business | Technology | Data Science |
| 1 | Switzerland | 96% | 99% | 77% |
| 2 | Spain | 48% | 100% | 97% |
| 3 | Germany | 93% | 84% | 92% |
| 4 | Luxembourg | 98% | 58% | 95% |
| 5 | Japan | 27% | 92% | 98% |
| 78 | United States | 53% | 16% | 32% |
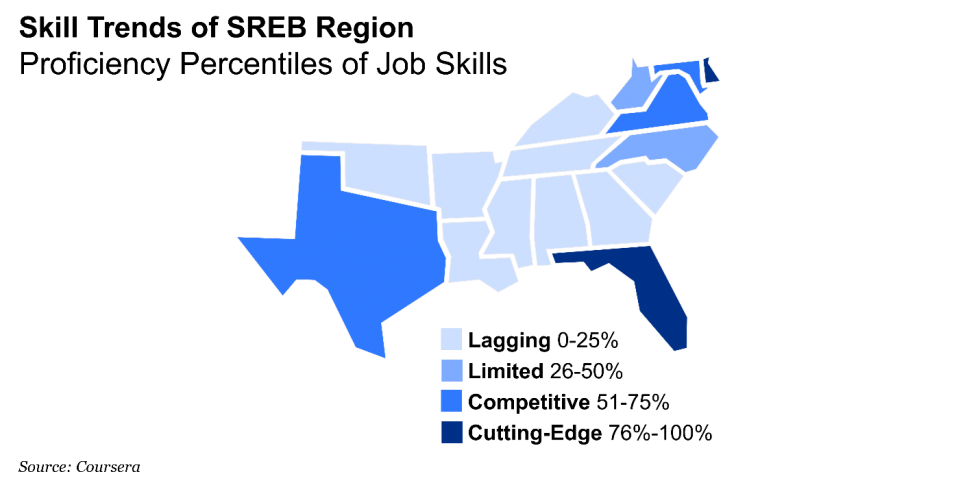
In order to calculate skill proficiency at the country level, Coursera measured the skill proficiency of each of its learners across each skill to then aggregate proficiencies for a country. Each country is then compared against one another by using a percentile ranking. These percentile rankings are divided into four proficiency categories:
- Cutting-edge: 76th percentile or above
- Competitive: 51st-75th percentile
- Limited: 26th-50th percentile
- Lagging: 25th percentile or below
While the overall United States is categorized as lagging, the performance of learners in SREB region falls further behind other regions in the US. Out of the region’s 16 states, only five were in competitive or cutting-edge percentile, with 11 states falling behind with limited or lagging percentiles in the vital job-skill domains of business, technology and data science.
The data from the report cannot represent the population entirely, as it is based only on Coursera registered learners. However, it does correlate to economic indicators such as economic growth being tied to skill proficiency. The SREB region will continue to lag behind based on individuals’ skill proficiencies.
States within the SREB region need to make large and concerted efforts to better prepare the workforce for the uncertain future of technology. SREB states’ efforts will need to be greater than the rest of the country if they hope to become competitive. Investments include helping low-skilled adults earn diplomas and helping working adults across the region keep up with technological advancements.
Watch for a new report on success skills this fall from SREB’s Dual Enrollment Initiative. The report analyzes how success skills are defined, which ones are in demand and important actions suggested by the research.