Topic: Workforce and Education
Education and the Workforce
Trends, Readiness and Preparation
A thriving workforce is at the heart of SREB’s mission to improve education and help states build robust economies.
Technology promises seismic shifts in the jobs of tomorrow. SREB is committed to helping state leaders find solutions to the challenge of preparing children, youth and adults for a changing workplace.
Recent SREB commissions have addressed how schools and colleges can prepare students for the world of work. Our analysts monitor data on educational attainment and workforce trends, and our school improvement programs help schools adopt high-quality career pathways.
Labor Market Data Hub
Connect education to local careers
Explore SREB’s interactive dashboard with detailed data on occupations in each SREB state and workforce region.
Students deserve a clear pathway to careers in their communities.
Local labor market data can help schools be sure the career pathways they offer lead to high-wage, high-demand, high-skill careers. See how your education programs connect to certificates, career pathways and state priorities.
The Skills Employers Demand
An Analysis of the Research
This report reviews the research on non-technical skills to identify the success skills employers most often seek. It summarizes relevant studies, skills gaps and credentialing to help policymakers, educators and businesses align efforts to prepare students for the workplace.
The Pandemic’s Dual Threat for Vulnerable Workers
Accelerated automation and post-pandemic impacts could displace millions
The COVID-19 pandemic presents a dual threat to vulnerable workers in the South. Accelerated automation and unemployment potential due to COVID-19 could impact the lives of millions.
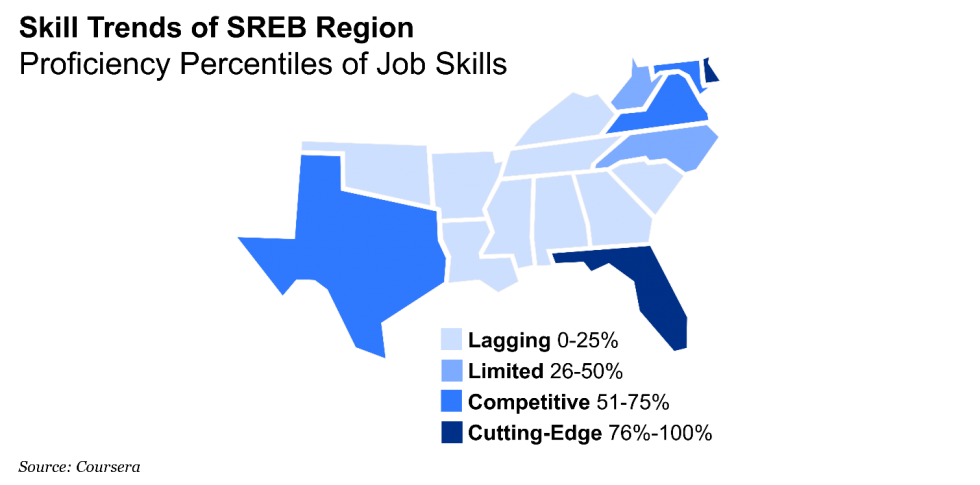
SREB Region Lags Behind in New Skills Report
In the new Coursera Global Skills Report, the United States ranked 78 out 100 countries on job skills observed from Coursera’s learner base. The three job-relevant skill domains compared in the report were business, technology and data science.
Early Pandemic Impacts Threaten the Region’s Workforce
In 2019, the Southern Regional Education Board projected that 18 million workers across the SREB region could become unemployable or stuck in low-wage jobs by 2030 if states did nothing to raise their skills to a postsecondary level.
COVID-19 Impacts on Child Care Providers and Families
Higher Costs, Lower Enrollment Threaten Availability
The COVID-19 pandemic has revealed—and exacerbated—challenges affecting our nation’s child care system. Many child care operators have struggled financially as they deal with shut downs, lower enrollments and increased costs.
A Conversation Among Governors
Education and Workforce Recovery
View the webinar recording
Southern governors discussed the central role of education in fueling growth through workforce and economic development. The conversation also covered spending priorities for federal relief funding and priorities for improving education.
Partnerships to Align Education and Careers
Report of the Commission on Strategic Partnerships for Work-Ready Students
This commission report offers a vision of education connected to local careers and shows how to make it a reality through partnerships and policy. With 11 recommendations to help states build strategic industry sector partnerships, the report covers policies, funding and building the capacity of educators. It also spotlights innovative solutions from around the nation.
Expanding Work-Based Learning Experiences
Tools and Mechanisms: Reach More Students Using Technology
View the webinar recording
Preparing students to be career-ready is important and complex work. Educators, workforce development leaders, and industry representatives need simulated workplace programs and other virtual solutions to expand work-based learning opportunities in rural and hard-to-serve communities.
Opening Doors Through Work-Based Learning
Policies: Adopting Measures to Support Work-Based Learning
View the webinar recording
Work-based learning has been identified by many organizations and researchers as a necessary educational component or preparing students for success in adulthood. Kentucky has created a policy solution for challenges to work-based learning such as workers’ compensation and liability insurance.
Industry-Education Partnerships for Local Workforce Needs
Process: How to Forge Partnerships
View the webinar recording
Industry sector partnerships are an essential strategy for workforce development in states, as they bring business partners together with the public sector to guide the preparation of workers for the high-demand jobs most critical to local economies.
Help Businesses Prepare Workers to Fill Critical Positions
Bouncing Back From COVID-19 Using Education and Workforce Dollars
View webinar recording
In the fourth webinar in the Bouncing Back From Covid Using Education and Workforce Dollars series, SREB presenters discussed how state leaders can help businesses upskill new and longer-term employees to fill positions critical to the state’s economic recovery. SREB also spotlighted how states can address issues of equity and braid multiple funding sources to support this work. Leaders in Indiana shared their exemplary efforts in this area.
Make Education and Training Programs More Tech Savvy and Flexible
Bouncing Back From COVID-19 Using Education and Workforce Dollars
View webinar recording
In the fifth webinar in the Bouncing Back from COVID-19 Using Education and Workforce Dollars series, SREB presenters shared strategies for readying workers to succeed in workplaces that are increasingly technology dependent. They also discussed how education and training programs can leverage technology and flexible formats so they can maintain programs when traditional formats are not practical.
Connect Emergency Responses To Longer-term Workforce Efforts
Bouncing Back From COVID-19 Using Education and Workforce Dollars
View webinar recording
The sixth webinar in the Bouncing Back from COVID-19 Using Education and Workforce Dollars series covered how state leaders can ensure that their short-term emergency measures to address COVID-19 contribute toward achieving the state’s long-term vision for a thriving workforce and healthy economy. Presentations highlighted Alabama’s work in this area and included ways to align ESSA, Perkins V, WIOA, CARES Act and state and grant dollars.
Help Low-Skilled Adults Earn Credentials for Critical Jobs
Bouncing Back From COVID-19 Using Education and Workforce Dollars
View webinar recording
The second webinar in the Bouncing Back From Covid Using Education and Workforce Dollars series explores how states can help workers with low skills earn the credentials they need to secure and succeed at jobs critical to the state’s economic recovery. SREB presenters discussed strategies for targeting grants to individuals and postsecondary institutions and for addressing issues of equity.
Help Students Earn Credentials to Fill Critical Jobs
Bouncing Back From COVID-19 Using Education and Workforce Dollars
View webinar recording
The third webinar in the Bouncing Back From Covid Using Education and Workforce Dollars series covers strategies to help students gain postsecondary knowledge and skills to fill jobs critical to the state’s economic recovery. SREB presenters explored strategies for strengthening dual enrollment programs and helping new graduates maintain their educational momentum even when families struggle to afford tuition.
Gauge Workforce Frequently, Prioritize Action Together
Bouncing Back From COVID-19 Using Education and Workforce Dollars
View webinar recording
Presenters made the case for analyzing data in rapid cycles to identify actions to spark workforce improvements and keep an eye on equity. The webinar covered partners to engage, including industry-sector partnerships, and spotlights how states can braid multiple federal and state funding sources for the work.
Designing a Ready Workforce
Opportunities for state leaders to align ESSA, Perkins V and WIOA funds
To support states as they finalize their new Perkins V and WIOA plans and consider updates to their ESSA plans, SREB reviewed a sample of states’ existing plans and identified six ways states have missed opportunities in the past to align work funded by the three federal statutes. For each missed opportunity, SREB provides questions for policymakers to consider and gives examples from states of well-aligned plans.
The SREB Region’s Economic Outlook
The Potential Impact of Automation and AI
As companies continue to incorporate new technologies, making machine learning and robotics common in almost all workplaces, more and more working adults need to adapt to computerized work activities. Many need to move into new jobs raising their skill levels, or they will be out of a job altogether. This policy brief examines the ways automation and artificial intelligence will impact the workforce and encourages states and industry leaders to act quickly to prepare employees for the workplace transformations.
Unprepared and Unaware
Upskilling the Workforce for a Decade of Uncertainty
This report examines how technology and automation are changing the job market — and what states can do to prepare adults for the new workplace. It analyzes shifts from low- to middle-skills jobs, details current education levels and offers recommendations for retooling adult education programs.
Workforce-Driven Financial Aid: Policies and Strategies
Essential Elements of State Policy For College Completion
The rapidly evolving workplace has created a shortage of skilled and educated workers in many fields, leaving essential jobs unfilled and millions of adults unqualified for them. This policy brief summarizes statewide strategies to support financial assistance for students in programs designed to address workforce needs. It includes suggestions for states that are evaluating, or considering creating, workforce-driven financial aid policies.
Effective Adult Education Programs: A Challenge for States
States face an uphill battle in meeting the needs of adult learners, especially at a time when technology is advancing rapidly. Adults can turn to adult education programs to improve their skills, but enrollments have fallen in recent years.
Adapting Education, Keeping Pace with Automation
Technology is advancing at unprecedented rates. Though there have been grand transformations in information technologies, including computers, cell phones, automated services and customer-facing machines, these changes will likely be dwarfed by others in the coming decades. Automated vehicles and artificial intelligence have the capacity to reshape not only our workforce but our social and political systems. Machine learning will create work tasks in the future that can only be imagined today.
Three Federal Statutes, One State Plan
Coordinating ESSA, Perkins V and WIOA to address rapidly evolving education and workforce needs
This policy brief examines strategies to align state plans for three federal statutes, the Every Student Succeeds Act, Perkins V and the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act, to address rapidly evolving education and workforce needs and the steps states can take to streamline their K-12, CTE and workforce development systems.
A Unified Statewide Vision
Aligning ESSA, Perkins V and WIOA Across the Lifespan
The reauthorization of three federal statutes — the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act, the Every Student Succeeds Act and Perkins V — has given states the chance, and an unprecedented flexibility, to align all three in powerful ways. This brief includes questions that state legislators and other policymakers can ask to determine how to best implement them as one coherent system.
Report Urges Action to Narrow 2030 Skills Gap
States can retool adult education to prepare vulnerable workers
New report urges leaders to look a decade ahead and prepare their states for changes that threaten to leave millions unemployed and millions of jobs with no one to fill them.
Adult Education Attainment
SREB Fact Book Table 7
High school diploma, bachelor’s degree, 25 to 44 years, broken out by race/ethnicity and gender, 50 states and four regions
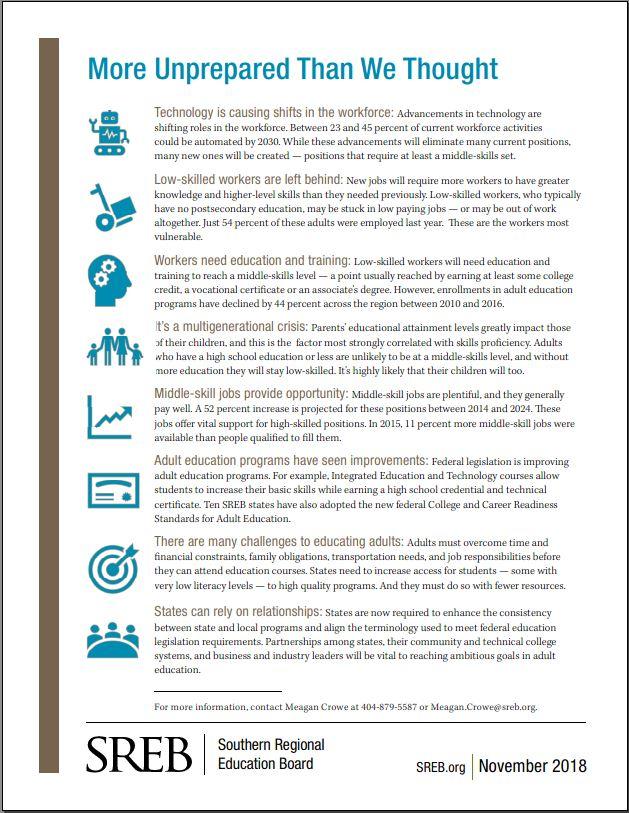
More Unprepared Than We Thought
Adult educational attainment
Low-skilled workers are being left behind as technology shifts the workforce toward the middle-skills level. Educators and policymakers will need to reach these adults with education and training to fill plentiful, well-paying middle-skill jobs in their states. This fact sheet summarizes trends and state policy concerns.
Postsecondary Attainment Goals
in SREB States
| State | 2019 Attainment Level |
Goal | By |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 45.1% | Add 500,000 high-skilled employees | 2025 |
| Arkansas | 43.6% | 60% | 2025 |
| Delaware | 47.9% | none | none |
| Florida | 52.8% | 55% | 2025 |
| Georgia | 52.8% | 60% | 2025 |
| Kentucky | 49.4% | 60% | 2030 |
| Louisiana | 48.1% | 60% | 2030 |
| Maryland | 55.9% | 55% | 2025 |
| Mississippi | 44.4% | Reach the national attainment level average | 2025 |
| North Carolina | 52.1% | Ensure that 2 million, age 25 to 44, have earned a postsecondary degree or credential | 2030 |
| Oklahoma | 46.5% | 70% | 2025 |
| South Carolina | 47.6% | 60% | 2025 |
| Tennessee | 46.8% | 55% | 2025 |
| Texas | 47.9% | 60% of adults ages 25-34 | 2030 |
| Virginia | 57.4% | 70% | 2030 |
| West Virginia | 42.6% | 60% | 2030 |
Inspiring Students to Explore STEM with SREB’s Advanced Career Courses
How AC’s nine pathways connect classrooms, college and the careers of the future
As you know, science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) skills are in high demand in today’s fast-paced, technology-driven economy. Leading employers prize job candidates with strong communication and teamwork skills who anticipate workplace problems and can apply literacy, math and technical know-how to solve them. (Learn more in this Business Roundtable report).
Bridging the Computer Science Education Gap
Five actions states can take
The Report of the SREB Commission on Computer Science and Information Technology
SREB’s Commission on Computer Science and Information Technology offers five actions for states and schools to help more young people — especially girls, black and Hispanic students, and students from low-income families — learn computer science and explore and choose careers in computing fields.
Credentials for All: An Imperative for SREB States
SREB’s Commission on Career and Technical Education offered eight actions states can take to build rigorous, relevant career pathways. Supported by policies and practices described in the report, these actions can help states increase the percentage of young adults earning valuable industry and postsecondary credentials.