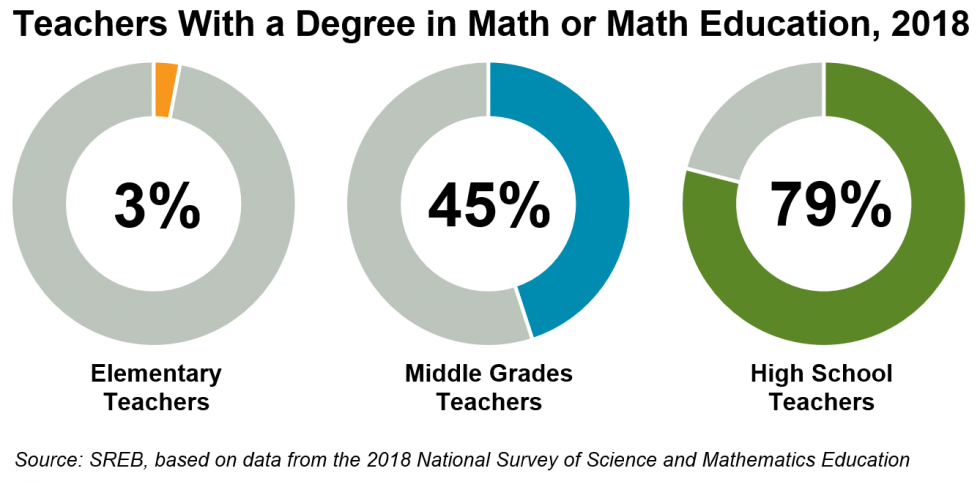Blog Main
Virtual Labs for STEM and CTE Teachers and Students
We know that this is a challenging time for teachers across the country. Many of you have been plunged into the world of virtual learning without a lot of time to prepare. Following sudden school closures due to the COVID-19 pandemic, you’ve had to move quickly to shift your carefully planned lessons online so your students can continue learning at home. And those of you who are STEM and career and technical education teachers in particular face unique challenges as you work to adapt hands-on learning experiences to a virtual format.
A Path to College and Career
Stepping Stones for States
A thriving economy and a workforce prepared for it will increasingly demand that more adults earn postsecondary credentials. Ensuring that students successfully move from middle grades into high school, then into college or technical education programs, is critical if states hope to boost their adult educational attainment levels.
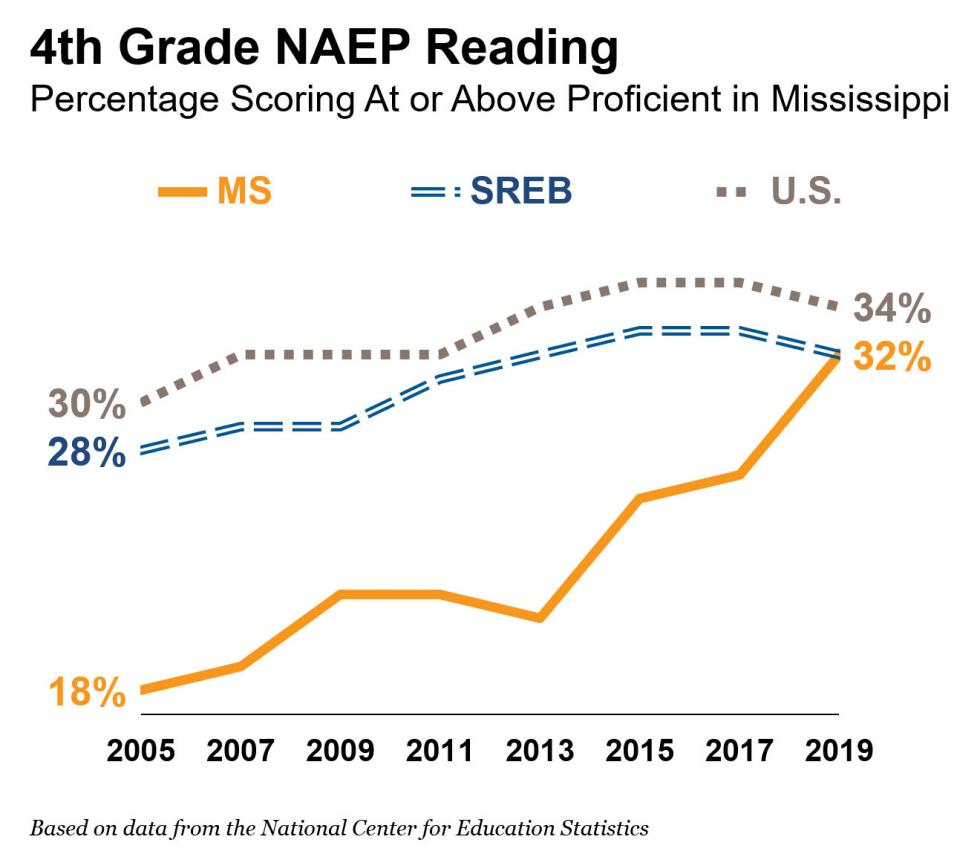
Thank Goodness for Mississippi
Star NAEP Showing Follows a Long Commitment
“Thank goodness for Mississippi.”
It used to be that this was something you heard from people who were grateful that Mississippi kept their own states from the dubious honor of last place in education rankings. Those folks may not have noticed that, since 2005, Mississippi has been making steady gains.
And now, after Mississippi offered a rare bright spot on the Nation’s Report Card earlier this month, we have a new reason to be thankful for Mississippi: We can learn from their success.
Real progress takes time.
How Can a Roundtable on Education Human Capital Help Your State?
Another school year has started, and nearly every state in the SREB region is facing major human capital challenges including teacher shortages. Schools now face shortages not only in STEM courses and special education but in most subject areas.
Effective Adult Education Programs: A Challenge for States
States face an uphill battle in meeting the needs of adult learners, especially at a time when technology is advancing rapidly. Adults can turn to adult education programs to improve their skills, but enrollments have fallen in recent years.
Using Data to Transform Teacher Preparation
The SREB Teacher Preparation Commission has called on state leaders to build data systems that will improve preparation programs. The commission identified three groups that would benefit from robust and accessible data:
- Individuals choosing where to enroll
- Preparation providers interested in improving their strategies
- Policymakers considering changes to state requirements
Adapting Education, Keeping Pace with Automation
Technology is advancing at unprecedented rates. Though there have been grand transformations in information technologies, including computers, cell phones, automated services and customer-facing machines, these changes will likely be dwarfed by others in the coming decades. Automated vehicles and artificial intelligence have the capacity to reshape not only our workforce but our social and political systems. Machine learning will create work tasks in the future that can only be imagined today.
Joan Lord Retires
Joan Lord has always put the and in “policy and practice.” In nearly twenty years at SREB, Lord has overseen policy research and analysis, worked with her share of policy commissions, and written innumerable policy briefs and recommendations, always with the second half of the pair — practice — firmly in mind. Policy is not, to her mind, an empty intellectual exercise but an action plan, a living document to improve the region’s education from top to bottom.
Making Sense of Changes to Teacher Preparation and Licensure
SREB state legislators introduced over 4,600 education bills in 2019 regular sessions. At least 850 of these bills will become law, with roughly one hundred this year relating to teachers and principals. Here’s how seven notable bills align with SREB’s Teacher Preparation Commission recommendations.
The Eisenhower Matrix: A Tool to Help School Leaders Focus Their Time
 The Eisenhower Matrix can help busy leaders make the most of their limited time to get things done. During World War II the matrix helped General Dwight Eisenhower plan and carry out the most complex military operation in history, the D-Day invasion of Normandy. He used it as a tool to ensure that he spent his time on the right work.
The Eisenhower Matrix can help busy leaders make the most of their limited time to get things done. During World War II the matrix helped General Dwight Eisenhower plan and carry out the most complex military operation in history, the D-Day invasion of Normandy. He used it as a tool to ensure that he spent his time on the right work.
Automation: Changing Jobs For Generations
Workforce changes are coming quickly, across the nation and especially in the South. In fact, they’re already here. Education and training across the SREB region will need to respond just as quickly to avoid severe economic outcomes.
Spotlight on Clinical Experiences
How State Leaders Could Support High-Quality Clinical Practice
The SREB Teacher Preparation Commission called on state leaders to consider ways to improve the quality of teacher candidates’ classroom experiences. After consulting the research, Commission members learned that the length of a clinical experience is less important than ensuring that candidates are supported by effective mentors and supervised by university faculty who have experience in the classroom.
Giving Elementary Teachers the Tools to Teach Math Well
Broad preparation can leave math-specific knowledge lacking
 It’s no secret that aspiring
teachers with strong math backgrounds tend to be drawn toward the
secondary grades, where they can just teach math. In fact,
results of the 2018 National Survey of Science and Math
Education showed that just 3 percent of elementary teachers
surveyed held a degree in mathematics or math education, compared
with 45 percent of middle grades math teachers and 79 percent of
high school math teachers.
It’s no secret that aspiring
teachers with strong math backgrounds tend to be drawn toward the
secondary grades, where they can just teach math. In fact,
results of the 2018 National Survey of Science and Math
Education showed that just 3 percent of elementary teachers
surveyed held a degree in mathematics or math education, compared
with 45 percent of middle grades math teachers and 79 percent of
high school math teachers.
Educator Effectiveness is About Learning and Growth Opportunities
And that should never end
Lessons learned from three years of work in 8 states
 Providing real-time feedback and
growth opportunities to teachers — the real purpose of educator
effectiveness systems — means that school leaders have to
understand and value the skills to be instructional leaders
and be properly trained on those skills. In any career
path, professionals need to know how they’re doing and need help
honing their craft. Teaching is no different; teachers need a
coach, they need feedback.
Providing real-time feedback and
growth opportunities to teachers — the real purpose of educator
effectiveness systems — means that school leaders have to
understand and value the skills to be instructional leaders
and be properly trained on those skills. In any career
path, professionals need to know how they’re doing and need help
honing their craft. Teaching is no different; teachers need a
coach, they need feedback.
Why Do We Say “I’m Bad at Math”?
How math anxiety affects performance, and what we can do about it
We’ve all likely heard someone say, “I’m bad at math,” or even “I hate math.” In the United States, math is too often considered a subject that either comes naturally or doesn’t — there are “math people,” and everyone else can expect to struggle with it. If you stop and think, though, this makes as much sense as saying we’re all naturally good (or bad) at sports, or music, or writing. It’s true that becoming skilled in any of these areas may come more easily to some people than others, but we generally understand that no one becomes expert at baseball without learning the game and spending a lot of time practicing.
Update on Final Legislative Actions in VA, WV
While the first and second Legislative Report issues of the year are focused on gubernatorial budget proposals, several SREB states have already completed their 2019 regular legislative sessions — the first ones across the finish line being Virginia and West Virginia. Here is a brief summary of final actions in both states; we’ll have full write-ups on final actions in all 16 SREB states in coming blog posts and Legislative Report editions.
Getting the Balance Right
Reconsidering the Mix of Teacher Licensure Measures
The SREB Teacher Preparation Commission called on state leaders to adopt practice-based assessments. These tests assess candidates’ readiness to lead a classroom and to apply lessons learned during coursework and clinical experiences.
Practice-based assessments have diagnostic value, meaning they provide performance data that educator preparation programs can use to identify strengths and opportunities for improvement. State agencies could use the assessment data to determine how they will provide technical assistance to preparation programs.
Teacher Salary Proposals
SREB states, 2019 and 2018
Teacher salaries are in the news, and we’ve been getting some questions about what actions SREB states are taking during this year’s legislative sessions. Here are proposals so far in 2019. Bonus: 2018 actions.
Cyberattacks: Helping Schools Fight Back
Nearly 60 percent of U.S. school districts report cyberattacks infrequently — every month or less, according to a recent Consortium for School Networking report. But in November, David Couch, K-12 Chief Information Officer at the Kentucky Department of Education, made a startling announcement. Couch told the SREB Legislative Advisory Council that he’d seen over 4 billion attempted cyber-attacks in one year in his state.
In This Together: How States Foster Safe Learning Environments
As legislatures convene regular sessions, we at SREB have observed an uptick in bills focused on school safety. Some propose dramatic changes in the way school districts hire and train security personnel, develop emergency plans, or address students’ mental and emotional health. Others make technical changes to standing laws in order to lower the barriers districts face in creating safe learning environments.